Gait analysis is the systematic assessment of human locomotion, encompassing the study of how individuals walk or run. It involves examining the biomechanics and physiological aspects of movement to understand various patterns and abnormalities. This process is crucial in clinical settings, sports medicine, and rehabilitation programs, where it aids in diagnosing musculoskeletal disorders, neurological conditions, and developmental issues. The importance of the gait analysis of gait lies in its ability to provide valuable insights into functional limitations, assess treatment efficacy, and guide therapeutic interventions. Its objectives include improving mobility, enhancing performance, preventing injuries, and promoting overall well-being. By analyzing parameters such as joint angles, muscle activation patterns, and temporal-spatial characteristics, the gait analysis of gait facilitates personalized approaches to healthcare and rehabilitation, ultimately contributing to better outcomes for patients and athletes alike.
Anatomy And Physiology Of Gait
In the anatomy and physiology of gait, several key components play critical roles. Firstly, the process of walking engages a complex interplay of muscles throughout the body, including those in the legs, hips, core, and even upper body. Muscles such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteal muscles, and calf muscles work in coordination to provide stability, propulsion, and balance during each step. Secondly, biomechanics governs the mechanical principles underlying walking, encompassing forces, motion, and structural aspects. These biomechanical principles dictate how forces are transmitted through bones, joints, and soft tissues during locomotion, influencing factors such as stride length, step width, and foot placement. Finally, the gait cycle consists of distinct phases that delineate the sequence of movements involved in walking, including the stance phase (heel strike, midstance, toe-off) and the swing phase. Each phase involves specific muscle activations and joint movements, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of walking. Understanding these aspects of anatomy, physiology, and biomechanics is essential for comprehensively analyzing and interpreting gait patterns and abnormalities.
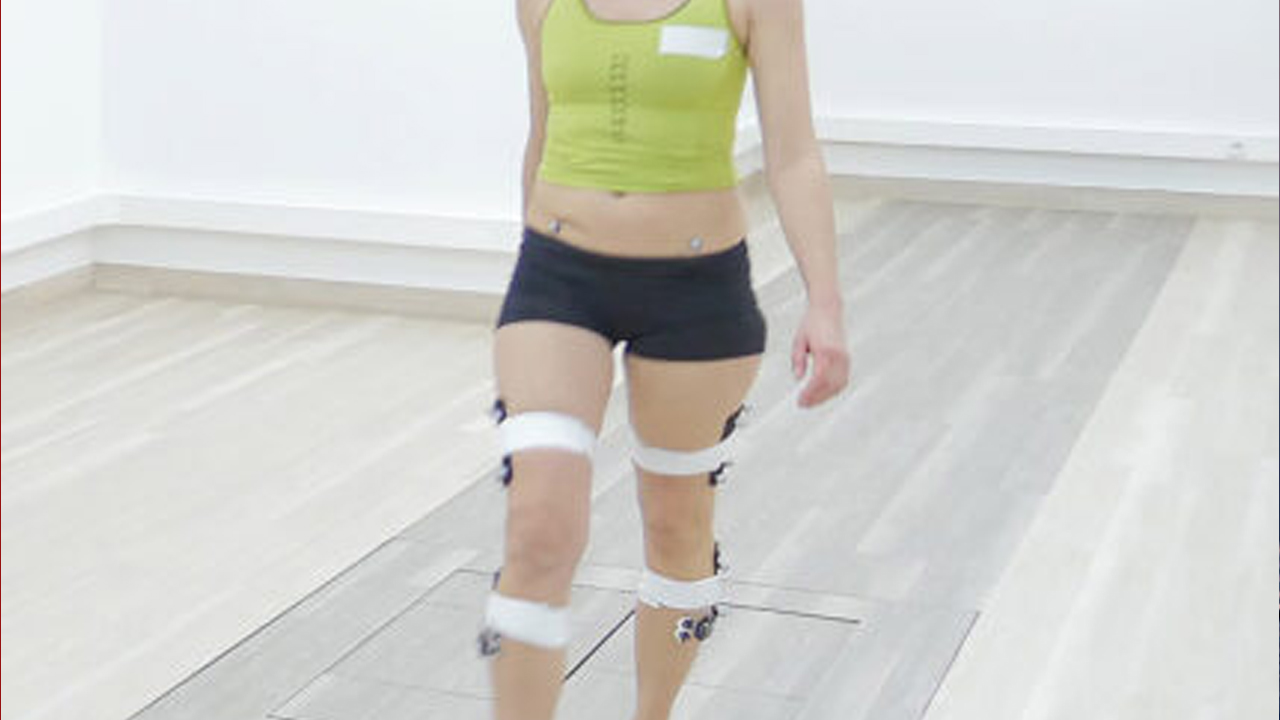
Methods Of Gait Analysis
Methods of analysis of gait encompass a range of approaches, including both traditional and advanced techniques. Visual observation serves as a fundamental method, where clinicians and researchers visually assess gait patterns and abnormalities. However, for a more precise and detailed analysis, instrumented methods are utilized. Motion capture systems utilize cameras to track the movement of reflective markers placed on the body, providing accurate kinematic data. Force plates measure ground reaction forces and moments, offering insights into kinetics and balance. Electromyography (EMG) records the electrical activity of muscles during movement, aiding in understanding muscle recruitment patterns. Pressure sensors assess the distribution of forces under the foot, helping to detect abnormalities in weight-bearing. Additionally, wearable sensors, such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, offer the advantage of assessing gait in real-world environments outside of the lab. Each method has its strengths and limitations, and the choice depends on the specific research or clinical objectives and available resources.
Clinical Applications Of Gait Analysis
Gait analysis finds extensive clinical applications across various medical disciplines, each benefiting from its insights in distinctive ways. In orthopedics, gait evaluation is pivotal for diagnosing and managing joint pathologies, offering detailed assessments of gait deviations associated with conditions like osteoarthritis or ligament injuries. Furthermore, it aids in post-surgical assessments, enabling clinicians to monitor recovery progress and functional outcomes following orthopedic interventions. In neurology, analysis of gait plays a crucial role in stroke rehabilitation, helping to assess gait impairments, track progress, and guide rehabilitation strategies to improve mobility and independence. Similarly, in Parkinson’s disease and spinal cord injuries, assessment of gait facilitates objective evaluation of motor deficits and assists in designing tailored interventions to optimize gait analysis function and quality of life. In pediatrics, analysis of gait is instrumental in diagnosing and managing developmental disorders such as muscular dystrophy or limb length discrepancies, as well as cerebral palsy, aiding in treatment planning and monitoring progress over time. Lastly, in sports medicine, analysis of gait serves dual roles: enhancing athletic performance by identifying biomechanical inefficiencies and optimizing training programs, and preventing injuries by detecting and addressing gait abnormalities or imbalances before they lead to overuse injuries or musculoskeletal issues. Overall, analysis of gait significantly contributes to improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of care across a wide spectrum of clinical settings.
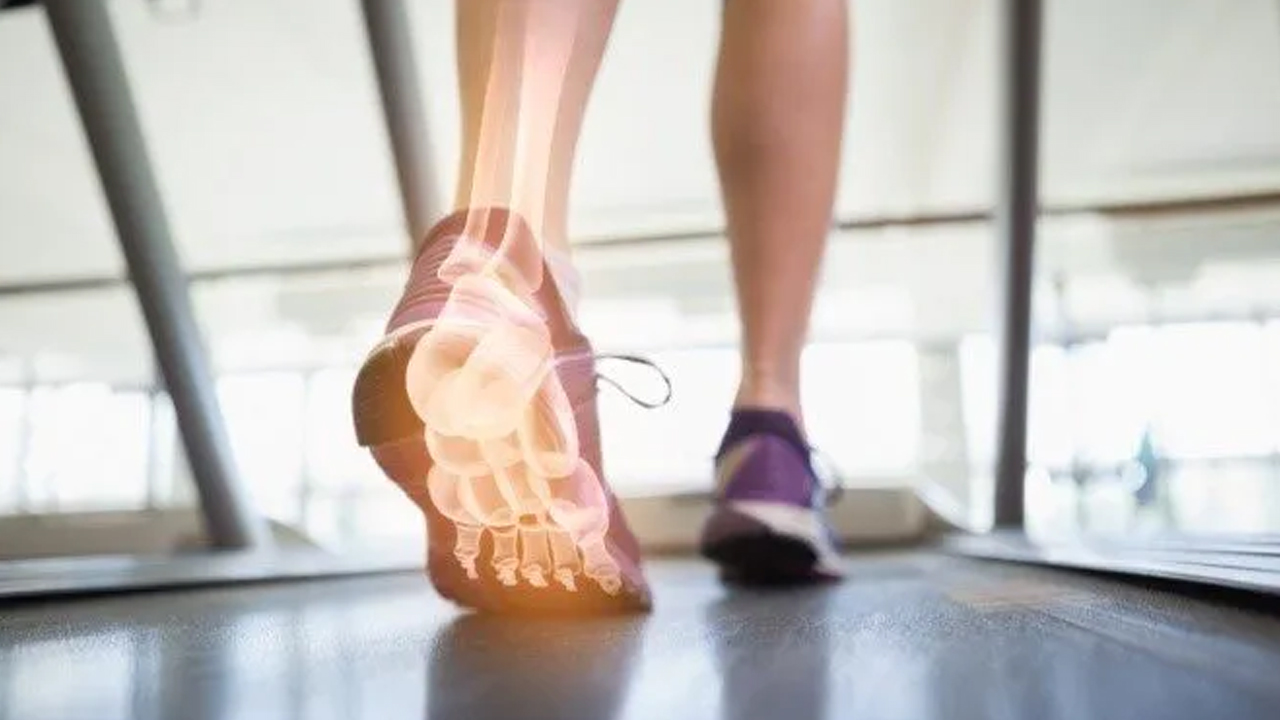
Interpretation Of Gait Analysis Data
Interpretation of gait data involves analyzing various parameters to gain insights into biomechanical and physiological aspects of movement. Kinematic parameters focus on joint angles, segmental motion, and body positions throughout the gait cycle, providing information about the quality and efficiency of movement. Kinetic parameters involve the measurement of forces and moments acting on the body, such as ground reaction forces and joint moments, which help to assess loading patterns and balance distribution during walking. Temporal-spatial parameters include metrics like stride length, cadence, and gait velocity, offering insights into the timing and coordination of gait events and identifying deviations from normal patterns. Muscle activation patterns, measured through electromyography (EMG), reveal the timing and intensity of muscle recruitment during gait, aiding in understanding muscular coordination and identifying potential weaknesses or imbalances. By integrating and analyzing these data sets, clinicians and researchers can comprehensively evaluate gait patterns, identify abnormalities, and tailor interventions to improve mobility, function, and overall quality of life.
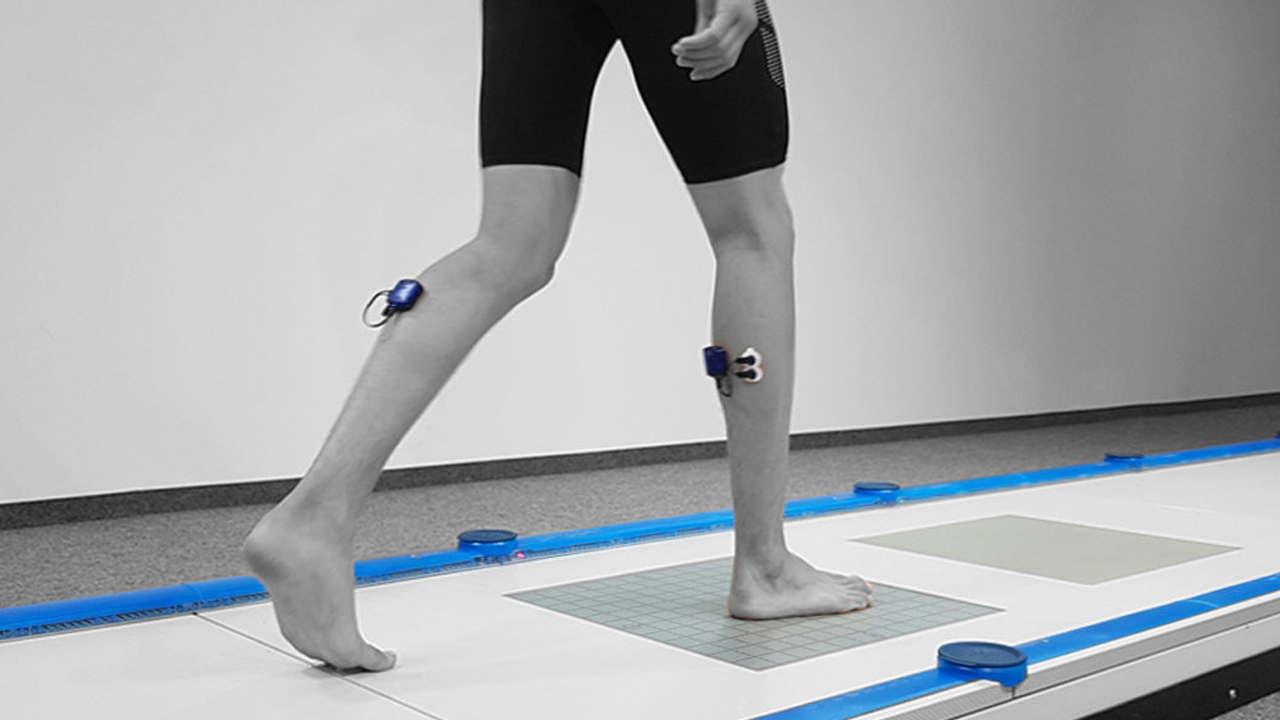
Challenges And Limitations
Despite its numerous benefits, gait analysis encounters several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. Cost and accessibility pose significant barriers, as advanced instrumentation and specialized expertise required for comprehensive analysis may be expensive and not readily available in all healthcare settings, limiting access to this valuable tool for certain populations. Interpretation complexity is another hurdle, as the analysis of gait data can be intricate and multifaceted, requiring trained professionals to accurately interpret and translate findings into meaningful clinical insights. Moreover, variability in gait patterns among individuals presents a challenge, as norms and reference values may not always apply universally,
necessitating careful consideration of individual characteristics and functional goals. Ethical considerations also arise, particularly concerning patient privacy, consent, and potential stigmatization associated with the diagnosis or labeling of gait abnormalities. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for expanding the reach and impact of the analysis of gait in improving patient care and advancing our understanding of human locomotion.
Future Directions
The future of gait analysis holds promise, with several potential directions for advancement. Firstly, technological innovations are expected to revolutionize the field, with advancements in motion capture systems, wearable sensors, and imaging modalities enhancing data collection accuracy and efficiency. Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) presents another exciting avenue, where machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and provide personalized recommendations for treatment and intervention strategies. Personalized medicine approaches are also gaining traction, with the recognition that individual variations in gait biomechanics and physiology necessitate tailored interventions based on patient-specific characteristics and goals. Additionally, longitudinal studies tracking gait patterns over time are essential for understanding disease progression, treatment effectiveness, and predicting long-term outcomes. By harnessing these advancements and embracing interdisciplinary collaborations, the future of the gait analysis of gait holds great potential for improving patient care, advancing scientific knowledge, and optimizing outcomes in rehabilitation and sports medicine.

Conclusion
In conclusion, gait analysis emerges as a crucial tool in healthcare and rehabilitation, offering valuable insights into human locomotion that transcend traditional diagnostic approaches. Its importance lies in its ability to comprehensively assess biomechanical, physiological, and functional aspects of movement, aiding in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of a wide range of musculoskeletal, neurological, and developmental conditions. The potential impact of gait evaluation on healthcare and rehabilitation is significant, with the potential to optimize treatment outcomes, improve patient mobility and quality of life, and reduce the burden of musculoskeletal disorders and injuries. However, to fully unlock its benefits, further research and development efforts are warranted. This includes refining assessment techniques, enhancing accessibility, and expanding our understanding of the complex interactions between gait patterns, underlying pathologies, and treatment responses. By investing in ongoing research and fostering interdisciplinary collaborations, we can harness the full potential of gait evaluation to advance patient care, promote functional independence, and shape the future of healthcare and rehabilitation.
Experience the difference with Ridgefield Chiropractic & Wellness Center’s expert gait analysis near me services. Take control of your mobility and performance. Schedule your personalized assessment today and embark on a journey to optimal health and vitality. Step confidently into a better tomorrow with us.
